Smart Glasses Usability and Accessibility Challenges
The initial allure of smart glasses is undeniable—a “heads-up display” for reality packaged in a premium frame. However, the honeymoon phase usually ends the moment the demo does. Moving from a controlled environment to everyday life reveals a glaring disconnect. Between the constant hunt for a charging cable and the subtle social friction of wearing a camera on your face, the transition to wearable tech is far from seamless.Continue reading for more details about Smart Glasses Usability.
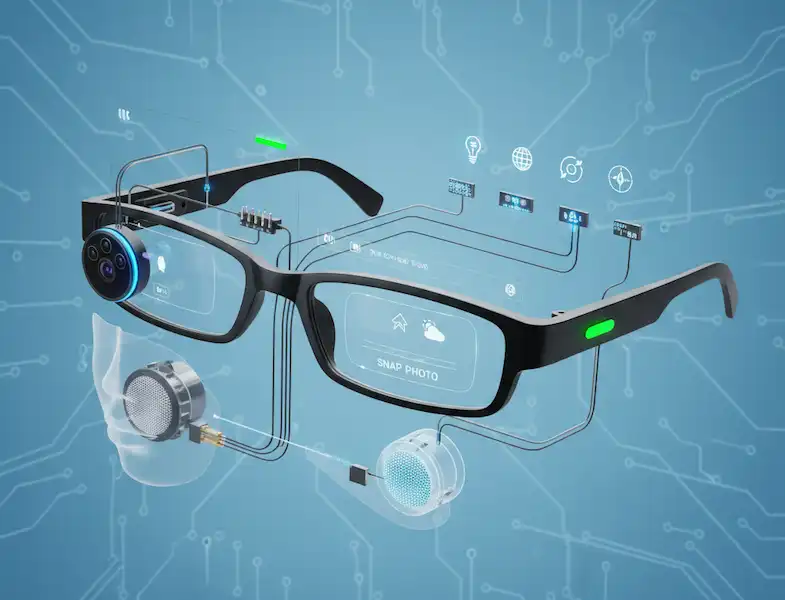
Usability isn’t just about whether the software works; it’s about whether the device earns its place on your face. After months of living with various models—from basic audio frames to full AR (Augmented Reality) displays—I’ve realized that smart glasses usability is a balancing act of ergonomics, social etiquette, and pure stamina.
The Weight of Innovation (Literally)
One of the first things you notice about Smart Glasses Usability is the weight. Standard prescription glasses usually weigh between 25 and 50 grams. Smart glasses, packed with batteries, processors, and cameras, can easily push past 75 grams.
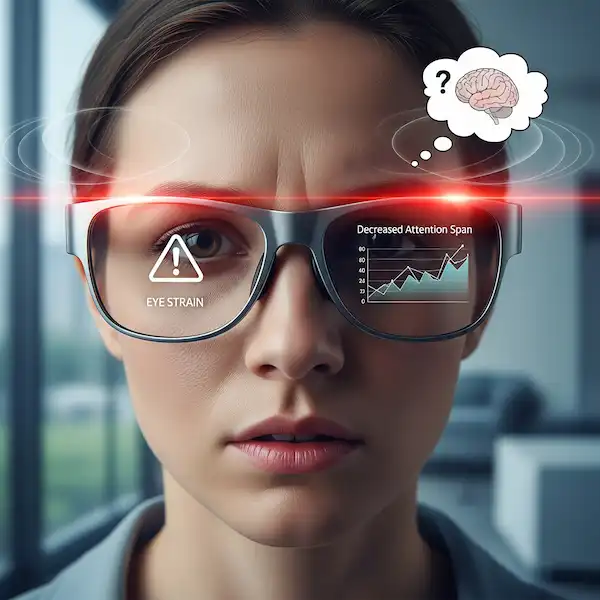
In my experience, the first hour feels fine. By hour three, you start feeling a distinct pressure on the bridge of your nose and a dull ache behind your ears. This is a classic ergonomic hurdle. Research into wearable ergonomics shows that even a few extra grams can drastically change user acceptance over a full workday. If they aren’t comfortable, they end up in the drawer.
The “Glasshole” Factor: Navigating Social Etiquette
I remember wearing a pair of camera-equipped glasses to a local coffee shop. I wasn’t recording, but the person across from me kept glancing at the corner of my frames, visibly uncomfortable. That’s the “Social Smart Glasses Usability” barrier.
Unlike a smartphone, which you physically pull out to use—signaling to others that your attention has shifted—smart glasses are always there. Am I looking at you, or am I reading a text message floating over your forehead? This ambiguity creates a power imbalance. To improve usability, many modern frames now include a bright, non-negotiable LED that shines when the camera is active, a design choice supported by privacy advocates to build trust between wearers and the public.
Interaction: Talking to Yourself in Public
How do you control a computer on your face? You generally have three options:
- Voice Commands: Great for when your hands are full (like cooking or driving), but incredibly awkward in a quiet elevator.
- Touchpads: Swiping the temple of your glasses looks like you’re deep in thought, but it can be finicky. I’ve accidentally hung up on my mom more times than I’d like to admit while trying to adjust my frames.
- Gesture/Gaze: Some high-end units track where you look. It feels like magic until a stray blink sends you into a settings menu you didn’t want.
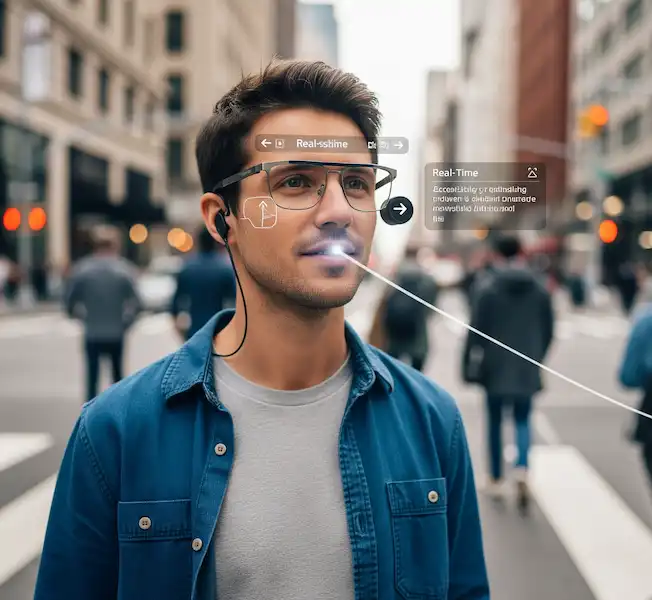
The shift toward Voice User Interfaces (VUI) is where the industry is heading. It’s about making the tech “invisible.” When I ask my glasses for directions while walking through a busy city, I’m not looking down at a screen. I’m engaged with the world, which is the ultimate goal of Smart Glasses Usability.
The Battery Life Struggle
If I’m honest, the biggest “usability killer” is the battery. Most AR glasses only last about 2 to 4 hours of heavy use. I’ve had my glasses die on me in the middle of navigating a hike, leaving me with essentially a very expensive, heavy pair of sunglasses.
Manufacturers are getting clever with charging cases—similar to Airpods—but the “all-day battery” remains the holy grail. Until we reach a point where a device can last 12+ hours, smart glasses will remain a “supplemental” tool rather than a smartphone replacement.
Visual Fatigue and “Cybersickness”
Living with a display inches from your eye isn’t natural. “Digital eye strain” is real. I found that during my first week, I’d get mild headaches after about two hours of use. Your brain has to learn how to focus on a digital overlay while simultaneously processing the physical world behind it.
Academic studies on Augmented Reality usability suggest that “focal depth” is the culprit. If the digital image feels like it’s at a different distance than the real world, your eyes constantly hunt for focus. Modern displays are getting better at mimicking natural focal points, but it’s still a hurdle for long-term wear.
Practical Tips for New Users
If you’re thinking about jumping into the world of smart glasses, here’s how I made them work for me:
- Curate Your Notifications: Don’t let every “like” or email pop up in your field of vision. It’s distracting and draining. Only allow high-priority alerts.
- Invest in Fit: If the glasses offer different nose pads, try them all. A secure fit is the difference between a tool and a nuisance.
- Mind the Room: If you’re in a private setting or a bathroom, take them off. It’s just common sense and helps normalize the tech for everyone else.
Best Use Cases 🎯For Usability and Accessibility
Despite the challenges, smart glasses usability are finding their footing in specific, high-value applications where the benefits of hands-free computing outweigh the drawbacks.
- Industrial and Manufacturing: Technicians can use smart glasses to receive step-by-step instructions overlaid on a machine, view real-time data, and get remote assistance from experts without taking their hands off their work. This boosts efficiency and safety.
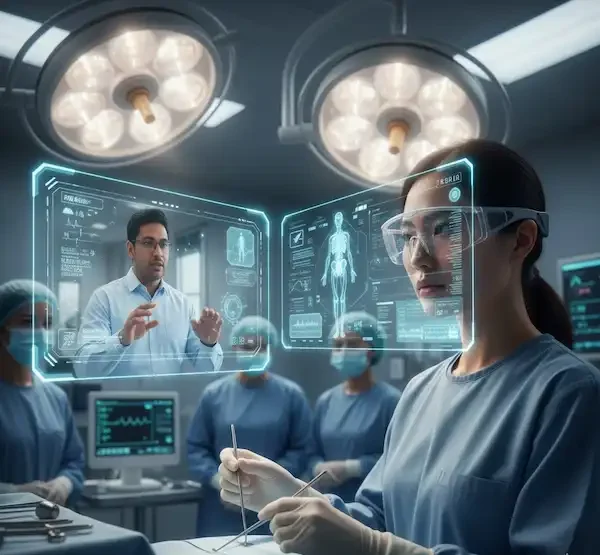
- Healthcare: Surgeons and medical professionals can use AR glasses to view patient data, such as X-rays or vital signs, during a procedure without looking away from the patient. Medical students can also use them for interactive, hands-on training.
- Logistics and Warehousing: Smart glasses can help workers with “pick-by-vision” systems, guiding them to the correct items in a warehouse and confirming selections, which reduces errors and speeds up the process.
- Accessibility for the Visually Impaired: Smart glasses equipped with AI and computer vision can describe surroundings, read text aloud, and assist with navigation for people with visual impairments, offering a new level of independence.
Troubleshooting Common Problems 🛠️
- My smart glasses won’t connect to my phone:
- Ensure Bluetooth is enabled on both devices.
- Make sure the companion app is updated to the latest version.
- Restart both the glasses and the phone.
- Check if your phone’s OS is compatible with the glasses’ software.
- The battery is draining too fast:
- Lower the display brightness.
- Limit the use of power-intensive features like video recording and continuous voice commands.
- Keep the device’s firmware updated, as these updates often include battery optimizations.
- Avoid using the glasses in extreme temperatures.
The Verdict
Smart Glasses Usability are at an awkward “teenage” phase. They are incredibly capable but still learning how to behave in public. For me, the freedom of a hands-free life—taking photos of my dog without fumbling for a phone or seeing a translation of a menu in real-time—outweighs the clunkiness. Usability is improving every year, and as the tech shrinks, it will eventually feel as natural as putting on a pair of Ray-Bans.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I get smart glasses with my prescription? A: Yes! Most major brands like Meta and XReal offer prescription lens inserts or allow you to have a local optician fit them. This is a huge win for usability, as you don’t have to “double up” on glasses.
Q: Do they get hot while you wear them? A: Sometimes. Because the processor is right next to your temple, they can get warm during intense tasks like video recording. Most have safety cut-offs, but it can be a bit startling the first time you feel it.
Q: Are they waterproof? A: Most are “water-resistant” (IPX4 or IP54), meaning they’re fine in light rain or sweat, but don’t go swimming with them. Always check the manufacturer’s IP rating before getting them wet.
Q: Can people see what I’m looking at on my display? A: Usually, no. From the outside, the lenses just look slightly tinted. However, in very dark rooms, there might be a tiny bit of “light leak” that someone sitting right next to you might notice.
Additional Helpful Content 🧠
- Learn more about Smart Glasses Accessibility – Smart Glasses Accessibility Tech & AR/VR
- Read about Smart Glasses prescriptions – Smart Glasses Prescription Lens & Diopter Adjustment Guide
- Smart Glasses Comparison – Cheap vs. Expensive Smart Glasses