What’s the Difference Between Cheap vs Expensive Smart Glasses
The world of smart glasses is evolving rapidly, offering a glimpse into a future where digital information seamlessly integrates with our physical reality. But with options ranging from budget-friendly models to high-end devices, how do you navigate the landscape? This smart glasses comparison comprehensive guide will break down the differences between Cheap vs Expensive Smart Glasses, help you determine if the investment is worthwhile, and explore their best use cases for both iPhone and Android users.
Why Most Comparisons Get It Wrong
I still remember the first time I wore a pair of smart glasses in public. It was a budget pair I’d found on sale, and I felt like I was living in a sci-fi movie—until I realized I was just wearing a clunky piece of plastic that died before my morning coffee was finished.
Since then, the market has exploded. We’ve gone from “Bluetooth speakers for your face” to actual AI-powered companions that can translate signs in real-time. But as I’ve learned the hard way (and through many drained batteries), the price tag doesn’t always tell the whole story. Whether you’re an iPhone devotee or an Android power user, choosing between a $100 entry-level pair and a $600 premium set is about more than just your budget—it’s about how much “tech friction” you’re willing to tolerate in your daily life. Continue reading to decipher the Cheap vs Expensive Smart Glasses comparisons and decide which way you want to go.
The “Cheap” Experience: Getting Your Feet Wet Without Drowning Your Wallet
When we talk about “cheap” smart glasses, we’re usually looking at the $100 to $250 range. Models like the first-gen Meta Ray-Bans or various “Smart Audio” frames fall into this category.
My Experience: The Gateway Drug
My first pair of budget frames was primarily for audio. I loved the idea of listening to podcasts while walking my dog without having earbuds blocking out the sound of approaching cars. This is where cheap glasses shine. They are fantastic “audio-first” devices.
The Pros of Going Budget:
- Safety & Awareness: Because they use open-ear speakers, you aren’t isolated from your environment.
- Simplicity: They usually just act as a Bluetooth headset. No complex AR overlays to calibrate.
- Durability (Sometimes): Surprisingly, some budget frames like the Solos AirGo 3 actually have better water resistance (IP67) than their $500 counterparts.
The “Gotchas”:
The build quality is where you feel the savings. Most cheap glasses use standard acetate or even lower-grade plastics. They feel a bit creaky. But the biggest deal-breaker? Battery life. On a cheap pair, if you’re taking calls and listening to music, you might only get 3 to 4 hours of active use. I once wore a budget pair to a conference, and they were dead before the keynote lunch.
The “Expensive” Experience: What Does $500+ Actually Buy You?
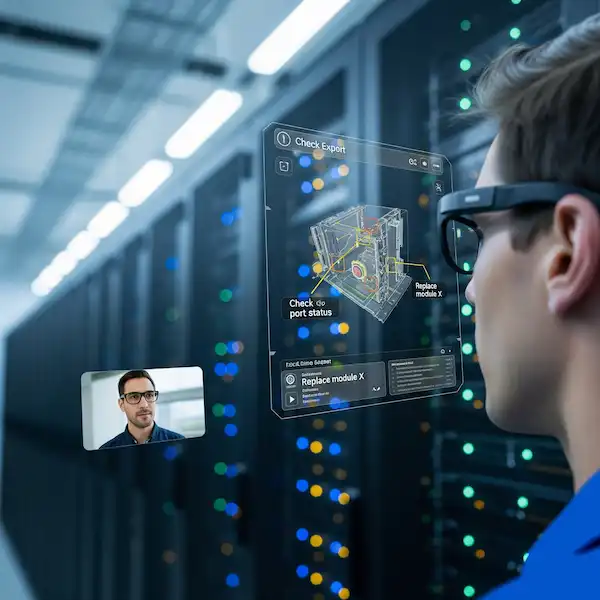
When you move into the $400–$700 tier (like the XREAL Air 2 Pro or the latest Ray-Ban Meta Gen 2), you aren’t just paying for a brand name. You’re paying for specialized hardware: Micro-OLED displays, waveguides, and dedicated AI processors.
The “Magic” Moment – Cheap vs Expensive
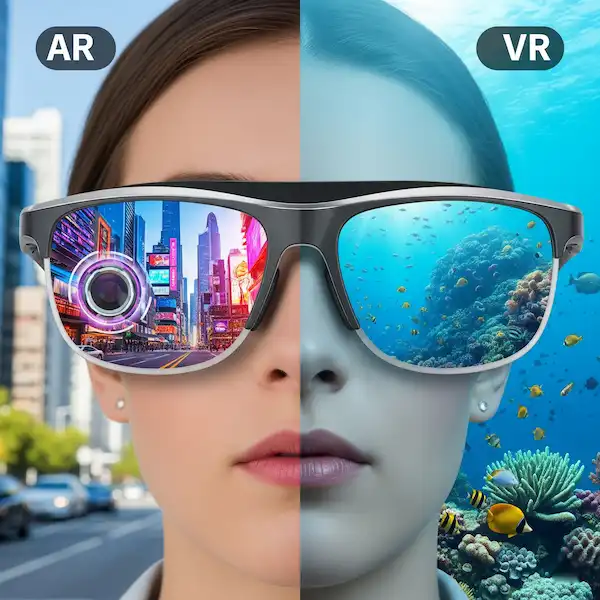
The first time I put on a pair of high-end AR (Augmented Reality) glasses, it felt fundamentally different. Instead of just hearing a notification, I saw a 130-inch virtual screen floating in the air. I could watch a movie on a plane while still seeing the flight attendant.
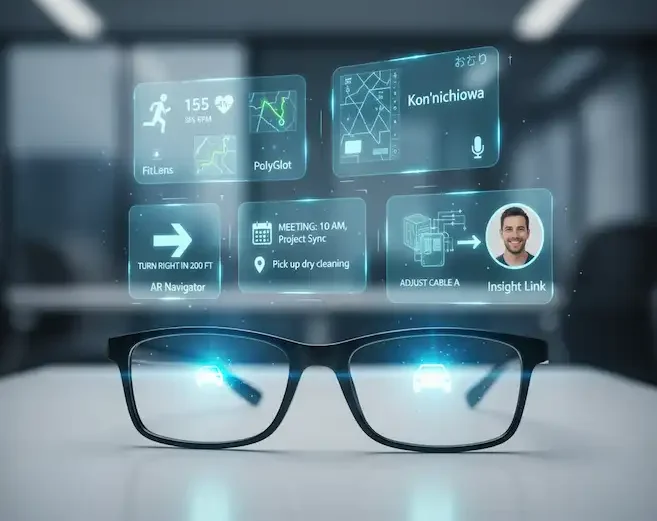
What You’re Actually Paying For:
- Display Technology: Premium glasses use Waveguide optics, which allow the lenses to stay thin and transparent while projecting crisp digital images.
- Multimodal AI: Expensive glasses often include cameras and NPUs (Neural Processing Units) that can “see” what you see. Asking your glasses, “What kind of plant is this?” and getting an instant answer feels like the future.
- Materials: High-end brands often use Titanium frames, which are hypoallergenic, lighter, and far more durable than plastic.
The Platform War: Android vs. iPhone Compatibility
This is the part where people get frustrated. Not all smart glasses play nice with every phone.
The iPhone Struggle (and Success)
If you’re on an iPhone, you’re locked into the Apple ecosystem’s rules.
- The Good: Apps for glasses on iOS are usually polished and stable.
- The Bad: Apple is protective of its hardware. For example, some AR glasses require a specific adapter for older iPhones with Lightning ports to handle video output (DP Alt Mode).
- My Tip: If you have an iPhone 15 or 16, life is easy because of the USB-C port. If you have an older model, check if the glasses require a “dongle” to work.
The Android Wild West
Android users generally have it easier with hardware connections (especially with Samsung’s DeX mode), but software can be hit or miss.
- The Good: Android phones often support “DisplayPort over USB-C” natively, meaning you can plug in AR glasses and immediately mirror your screen.
- The Bad: Some niche smart glasses apps are optimized for specific brands (like Samsung or Pixel) and might crash on others.
- My Tip: Always verify if the companion app is available on the Play Store and updated recently.
Features Face-Off: Cheap vs Expensive
| Feature | Cheap ($100 – $250) | Expensive ($300 – $700+) |
| Primary Use | Audio, Calls, Basic Notifications | AR Gaming, Movies, AI Vision, 3K Video |
| Display | Usually none (Audio only) | Micro-OLED, Virtual Screen up to 130″ |
| Camera | Rare (or low quality) | 12MP+ with stabilization |
| Battery | 3–6 hours (Active) | 4–12 hours (Varies by AR use) |
| Comfort | Can be bulky/heavy plastic | Often Titanium or lightweight Alloy |
| Prescription | Limited options | Integrated diopter dials or inserts |
Is It Worth It? My Final Recommendation
After testing everything from $50 “Amazon specials” to $3,000 enterprise headsets, here is my honest breakdown:
Buy the Cheap/Entry-Level Glasses if: You just want a better way to take calls and listen to music while staying present. If you’re a runner or a commuter who hates earbuds, a pair of $200 audio frames is a game-changer. You don’t need a screen to enjoy the convenience of a hands-free life.
Invest in the Expensive/High-End Glasses if: You travel a lot or want to replace your laptop screen. If you want the “AI assistant” experience—where your glasses can translate a menu in Japan or record a hands-free video of your kid’s first steps—you have to pay for the sensors.
My Personal Choice: I currently daily-wear the Ray-Ban Meta Gen 2s. They hit the “sweet spot” of looking like normal glasses while having an AI that actually works. Are they perfect? No. But they are the first pair that didn’t make me feel like a tech-support experiment gone wrong.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Do I need a prescription for smart glasses?
Not necessarily! Most smart glasses come with “plano” (non-prescription) lenses. However, if you wear glasses normally, you’ll want a pair that supports prescription inserts. High-end models like the VITURE Luma XR even have built-in “diopter dials” so you can adjust the focus without needing extra lenses.
2. Can people see what I’m seeing on the virtual screen?
No. Most premium AR glasses use “Waveguide” or “Birdbath” optics that project light directly into your pupils. From the outside, it just looks like you’re wearing slightly dark sunglasses.
3. How long do they really last?
This is the “marketing vs. reality” part. Manufacturers often claim “12 hours of use,” but they mean standby time. If you’re watching a movie in AR, expect 2 to 3 hours. If you’re just using them for occasional notifications and calls, you can usually make it through a full 8-hour workday.
4. Are they waterproof?
Most are “water-resistant” (IPX4), meaning they can handle a light drizzle or sweat. Very few are truly “waterproof” (IP67). If you’re a heavy sweater or live in a rainy city, double-check the IP rating before buying.
5. Will they work with my specific phone?
If your phone has a USB-C port and supports DP Alt Mode, it will work with almost all AR glasses. For iPhones older than the 15, you will almost certainly need an adapter. Android users should check if their phone supports “DisplayPort over USB-C” in the official specs.
Additional Helpful Links
- Smart Glasses Usability and Accessibility Issues
- Smart Glasses for under $100 – Best Smart Glasses Under $100: 2026 Comparison, Pros & Cons
External Links for Authoritative Sources
To delve deeper into the world of smart glasses and augmented reality, here are some reputable sources:
- IEEE Spectrum: A leading magazine from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, often features in-depth articles on emerging technologies like smart glasses. Search IEEE Spectrum for Smart Glasses
- Gartner: A global research and advisory firm providing insights into technology trends, including augmented reality and wearable devices. Gartner on Augmented Reality
- Statista: Offers comprehensive statistics and market data on various industries, including the smart wearables market. Statista on Smart Glasses Market
- MIT Technology Review: Explores the impact of new technologies. Search MIT Technology Review for Smart Glasses
- Augmented Reality Foundation: An industry association dedicated to advancing augmented reality.
By understanding these distinctions and considerations, you can make an informed decision about whether cheap or expensive smart glasses are the right choice for your needs in Cambodia and beyond. The technology is advancing rapidly, and as it matures, we can expect even more compelling and affordable options to emerge. The world of smart glasses is evolving rapidly, offering a glimpse into a future where digital information seamlessly integrates with our physical reality. But with options ranging from budget-friendly models to high-end devices, how do you navigate the landscape? This comprehensive guide will break down the differences between cheap and expensive smart glasses, help you determine if the investment is worthwhile, and explore their best use cases for both iPhone and Android users.