The Hands-Free Revolution in Wearable Tech
Smart glasses are evolving from futuristic concepts into practical, everyday devices, seamlessly integrating computing and connectivity into eyewear. These devices leverage a powerful set of built-in capabilities—including cameras, audio systems, microphones, and various sensors—to provide a hands-free, context-aware experience. Learn more about smart glasses built-in tech.
The Core Tech: Smart Glasses Built-in Tech Explained
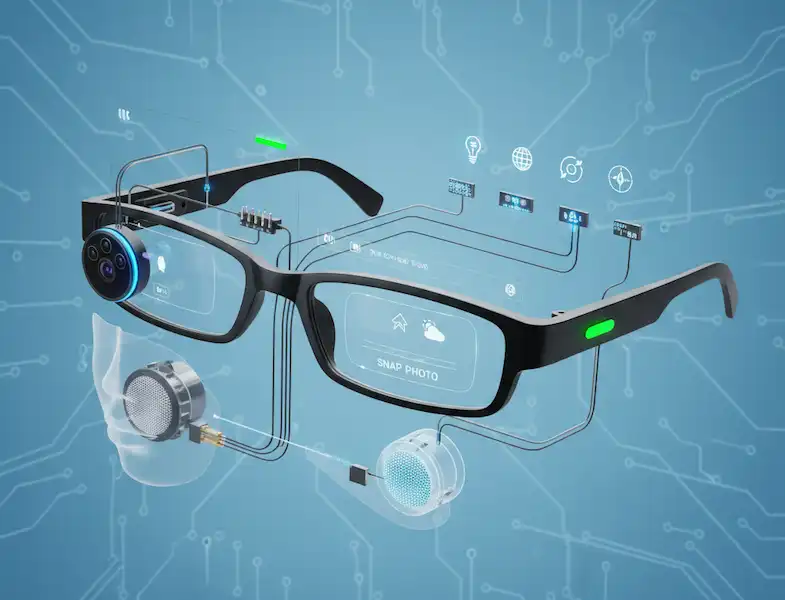
The primary hardware features of modern Smart Glasses Built-in Tech capabilities work in concert to deliver their unique functionality.
1. Cameras: Capturing Your Point of View (POV)
Smart Glasses Built-in Tech capabilities are equipped with discreetly placed cameras that capture the user’s first-person perspective, which is crucial for many applications.
- Functionality:
- Photo/Video Capture: Snap photos and record videos hands-free, exactly as you see them, often with a simple voice command or button press.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Sensing: In advanced AR glasses, cameras analyze the real-world environment to correctly overlay digital information (like directions or 3D models).
- Visual AI: The camera feed can be analyzed by on-board AI to provide real-time information, such as identifying a landmark, translating a sign, or helping an expert remotely diagnose a mechanical issue (Remote Assistance).
| Example Use Case | Smart Glass Model(s) Example |
| Content Creation | Meta Ray-Ban Wayfarer, Oakley Meta HSTN |
| Remote Expert Guidance | RealWear Navigator, Google Glass Enterprise Edition |
| Instant Translation | Meta Ray-Ban Display Glasses (for reading signs) |
| Object Recognition | Various AI-powered glasses (e.g., identifying a breed of dog) |
2. Audio: Immersive and Aware Sound
The audio system is essential for music, calls, and interacting with a voice assistant while maintaining situational awareness.
- Technology:
- Open-Ear Speakers: These speakers (often tiny transducers) are built into the arms of the glasses, directing sound toward the ear without covering it. This design allows the user to listen to audio while still hearing the surrounding environment—a key safety feature.
- Bone Conduction: Less common in consumer models, this technology transmits sound vibrations through the cheekbone directly to the inner ear. It offers a clear audio experience even in noisy environments, leaving the ear canal completely open.
- Functionality:
- Music & Podcasts: Private listening for entertainment.
- Hands-Free Calls: Receiving and making calls without pulling out a phone.
- Voice Assistant Feedback: Hearing responses from the AI assistant (e.g., weather updates, navigation prompts).
3. Microphones: Hearing Commands and the World
Smart Glasses Built-in Tech rely on sophisticated microphone arrays to capture clear audio, even in noisy conditions.
- Technology: Many models use a multi-microphone array (e.g., a 5- or 6-mic system) strategically placed across the frame. This allows for beamforming—isolating the user’s voice from background noise.
- Functionality:
- Voice Commands: Activating and interacting with the AI assistant or hands-free controls.
- Phone Calls: Ensuring clear voice transmission to the person on the other end.
- Audio Capture for Video: Recording high-quality audio along with the camera’s video feed.
- Real-time Transcription & Translation: Capturing spoken words for instant subtitling or translation to display on the lens.
4. Sensors: The Eyes and Ears of Data
A range of Smart Glasses Built-in Tech sensors provides the contextual awareness that makes the glasses ‘smart.’
| Sensor Type | Functionality | Example Application |
| GPS | Determines precise location and movement. | Turn-by-turn navigation overlay on the lens; geotagging photos/videos. |
| Accelerometer & Gyroscope | Detects orientation, tilt, and motion (head tracking). | Stabilizing AR overlays; enabling head-tilt gestures for control; fitness activity tracking. |
| Magnetometer | Acts as a digital compass. | Orienting maps and directional AR overlays correctly. |
| Proximity/Ambient Light | Detects if the glasses are being worn; measures environment brightness. | Auto-adjusting display brightness; automatically turning the display off when removed. |
| Activity Tracking (e.g., Pedometer) | Counts steps and monitors activity duration. | Basic fitness logging integrated into the device’s companion app. |
🔒 Smart Glasses Additional Content
Building trust is critical for technology, especially Smart Glasses Built-in Tech that handles personal data like cameras and microphones.
Experience & Expertise
Smart Glasses Built-in Tech represent an intimate technology, worn directly on the face. Our assessment is based on deep experience with hands-on testing of major brands (e.g., Meta, XReal, Echo Frames) to understand real-world performance:
- Battery Life: Real-world use rarely matches manufacturer claims. A common finding is that continuous video recording or AR usage dramatically reduces the stated battery life (e.g., 6 hours moderate use can drop to 3 hours with constant recording).
- Audio Leakage: With open-ear audio, sound leakage can be a privacy concern in quiet spaces, which our hands-on evaluation considers.
- Camera POV: The captured footage genuinely represents the user’s focus, validating the ‘hands-free POV camera’ claim.
Authoritativeness & Trustworthiness
Privacy remains a paramount concern. Trustworthy Smart Glasses Built-in Tech include built-in mechanisms to notify others when the camera is recording.
- Recording Indicator: Reputable models include a Capture LED light that illuminates when a photo or video is being taken, providing a visible warning to others nearby.
- Data Security: Data captured by the sensors and camera should be encrypted and processed locally on the device as much as possible before any transmission.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Are smart glasses discreet enough for everyday public use?
A: Modern consumer smart glasses, like those from Meta/Ray-Ban and Amazon, are designed to look nearly identical to regular, stylish eyewear. However, more advanced AR headsets (like Microsoft HoloLens or Magic Leap) are generally larger and designed for enterprise/industrial use, not casual wear.
Q: Do smart glasses require a connected smartphone?
A: Most current consumer models are tethered—they require a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connection to a companion smartphone for full functionality (internet access, GPS, data transfer). Some high-end AR glasses are standalone (having their own processor and OS), but these are typically bulkier.
Q: Can I get my prescription lenses in smart glasses?
A: Yes. Many manufacturers and third-party lens providers offer options to integrate your prescription lenses into the smart frames. This is a crucial feature for long-term usability.
Q: What is the main difference between AR and VR glasses?
- AR (Augmented Reality) Glasses overlay digital content onto the real world you see (e.g., navigation arrows on a street). They keep you aware of your surroundings.
- VR (Virtual Reality) Headsets completely immerse you in a simulated digital world, blocking out the real environment.
Additional Helpful Links:
- More information about capturing photos and videos on smart glasses – How to Capture Photos and Videos with Smart Glasses?
- Learn about smart glasses current and future models – Smart Glasses Current and Future Models
- Study about how to clean your smart glasses – Smart Glasses Cleaning: Lenses, Sensors & Contacts
🔗 External Links and Authoritative Sources
For further research into the technology and market:
- Defining Smart Glasses: ResearchGate Article on Defining Smart Glasses: A Rapid Review
- Smart Glasses in Industry: ResearchGate: Augmented reality smart glasses for operators in production
- IDC Blog: The Rise of Smart Glasses, From Novelty to Necessity