Smart Glasses in Professional/Enterprise Cases
Walking onto a bustling job site with a pair of high-end frames perched on my nose always brings a mix of excitement and a bit of “tech-jitters.” It’s one thing to see a slick marketing video of a technician effortlessly pulling up blueprints, but it’s quite another to be standing there in a high-vis vest, hands occupied with tools, trying to figure out if the device wants me to talk to it, tap it, or just nod like a bobblehead. The reality of using Smart Glasses for Business is that the hardware is only half the battle; the real magic happens when you master the invisible language of inputs—the swipes, the voice cues, and the subtle gestures that turn a wearable screen into a seamless extension of your workflow.
The Shift from Gadget to Tool
For years, smart glasses were the “next big thing” that never quite arrived for the average person. But in the industrial sector, the story is completely different. We aren’t looking for a way to check Instagram hands-free; we’re looking for ways to keep a mechanic from having to climb down a ladder ten times a shift to check a manual.
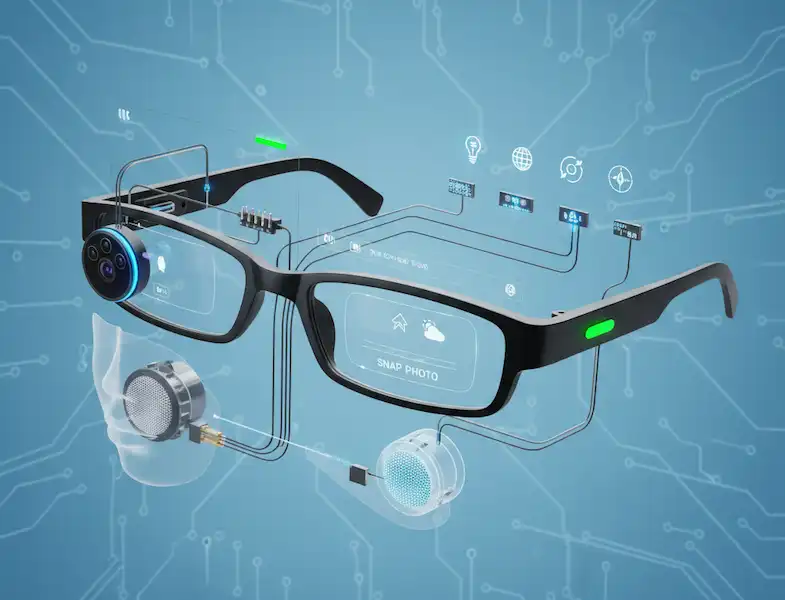
When we integrate Smart Glasses for Business, we are looking at three core pillars: See-What-I-See remote support, Digital Workflow instructions, and Real-Time Data Overlay.
I’ve spent time in deep-freeze warehouses where tablets literally freeze and die. I’ve watched workers try to juggle a clipboard and a scanner while climbing racking. It’s inefficient and, frankly, a bit dangerous. Transitioning these teams to an AR solution isn’t just about the “cool factor”—it’s about getting the data out of their hands and into their line of sight.
Industry-Specific AR Solutions
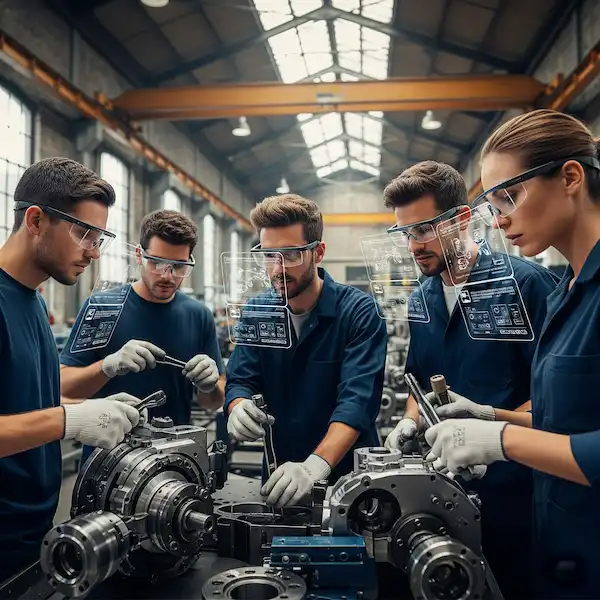
1. Manufacturing and Assembly
In the manufacturing world, “error proofing” is the holy grail. I recently worked with a line that assembled complex wiring harnesses. Traditionally, the workers had to look at a monitor, memorize a sequence, and then look back at the board.
With Smart Glasses for Business, we overlay a digital “ghost” image directly onto the physical board. The glasses literally point to the exact peg where the wire needs to go.
- Insider Knowledge: The biggest hurdle in manufacturing isn’t the software; it’s the “PPE” (Personal Protective Equipment) compatibility. If your glasses don’t clip onto a standard 3M hard hat or fit under a welding shield, they won’t be used. Brands like Vuzix and RealWear have dominated here because they built for the helmet first, and the eyes second.
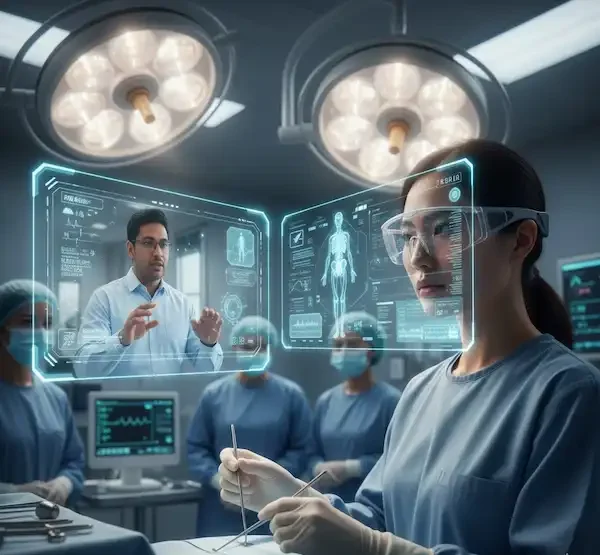
2. Healthcare and Surgical Assist
This is where the tech gets incredibly precise. Surgeons are using AR to see patient vitals or MRI scans superimposed near the surgical site.
- The OS Factor: In healthcare, the choice between Android and iPhone (iOS) hubs is often dictated by security. While Android allows for more custom hardware tweaks, many hospitals lean toward the iOS ecosystem because of its “closed-loop” security model and the ease of managing devices via a central MDM (Mobile Device Management) system.
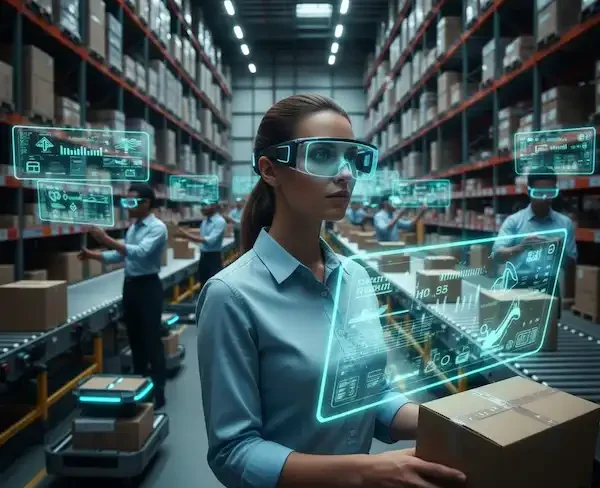
3. Logistics and Warehousing
“Vision Picking” is the term we use here. Instead of a handheld “gun” scanner, the glasses use their onboard camera to scan barcodes as the worker looks at the box.
- A Personal Lesson: I once saw a team try to deploy glasses with a 4-hour battery life for an 8-hour shift. It was a disaster. For Smart Glasses for Business in logistics, you need hot-swappable batteries. If you have to take the glasses off to charge them, the worker will just go back to their old, reliable paper list.
The Platform Dilemma: Android vs. iPhone
If you’re the person in charge of buying 50 pairs of glasses for your team, you need to know that the “brain” of the operation usually lives in the pocket.
The Android Advantage: Most enterprise-grade glasses (like the Vuzix M-Series or RealWear) actually run a modified version of Android internally. This makes the connection to an Android smartphone almost seamless. You can “sideload” proprietary APKs (apps) that aren’t on the public store, which is vital for internal company secrets.
The iPhone Experience: Apple’s “Made for iPhone” (MFi) program is rigorous. If a pair of glasses is officially supported by iOS, you can bet the connection will be stable. However, Apple is protective. You might find it harder to get deep “system-level” data from the phone to appear on the glasses compared to the open-source nature of Android.
Remote Mentoring: The “Killer App”
If there is one thing that justifies the cost of Smart Glasses for Business instantly, it’s “Remote Mentoring.”
Imagine your most senior engineer is in Germany, and a machine breaks down in Ohio. Instead of flying the engineer out, a local tech puts on the glasses. The engineer in Germany sees exactly what the tech sees in 4K resolution. They can “draw” on the tech’s screen—putting a red circle around the specific bolt that needs turning.
I’ve seen this save companies $20,000 in travel costs and downtime in a single afternoon. It turns every junior technician into an expert by proxy.
FAQ: The Questions I Get Asked Most
Q: Are they heavy? Will they give my employees headaches? A: Ten years ago, yes. Today, enterprise models are designed for “shift-long wearability.” The weight is often balanced toward the back of the head or clipped to a hat. However, I always recommend a “fit test.” Everyone’s face is shaped differently, and what’s comfortable for one person might pinch another’s nose.
Q: Can we use these in the rain or in a dusty factory? A: You need to look for an “IP Rating” (Ingress Protection). For Smart Glasses for Business, I wouldn’t touch anything less than IP66 for outdoor or industrial use. This ensures they are protected against dust and powerful water jets.
Q: How do we manage the software updates for 100 pairs of glasses? A: This is where Android shines. Using a system like Vuzix Manage or a standard MDM (Mobile Device Management), you can push updates to the entire fleet over Wi-Fi overnight, just like you would with company laptops.
Q: Do they work with prescription lenses? A: Absolutely. Most business-grade wearables offer “prescription inserts.” You simply take the insert to any optician, get your lenses fitted, and snap them into the frames.
Q: Is the “Smart Glasses for Business” market ready for small companies? A: It’s getting there. The “Remote Assist” software is now available on a subscription basis (SaaS), making the entry cost much lower than it used to be when you had to build your own custom software.
Summary of the Business Case
The era of “experimenting” with AR is over. We are now in the implementation phase. Whether it’s reducing the “time-to-competency” for new hires or eliminating travel costs for experts, Smart Glasses for Business provide a tangible return on investment that tablets and smartphones simply can’t match.
When you remove the friction of a handheld device, you empower your workforce to do what they do best: work with their hands, solve problems, and stay focused on the task in front of them. It’s not about adding more digital noise; it’s about providing the right information at the right moment.
Additional helpful information
- Smart Glasses in the future is worth waiting for – The Future of Smart Glasses – What is coming?
- Learn more about using smart glasses in healthcare – Smart Glasses in Healthcare: Enhancing Medical Practice
External Resources & Authority Links
- Vuzix Enterprise Solutions – A leader in the “Smart Glasses for Business” space.
- RealWear Ruggedized Wearables – The gold standard for heavy industrial environments.
- The Augmented Reality for Enterprise Alliance (AREA) – A fantastic resource for case studies on ROI and safety.
- Apple’s Vision Pro for Business – While more “spatial computing” than simple smart glasses, it’s where the high-end market is moving.